The Internet, cloud computing and mobile solutions have empowered people with the freedom and flexibility to do their jobs more easily and quickly than ever before. At the same time, new technologies continue to expand the volume and variety of data at our fingertips, enabling us to create and share information in new ways.
Technology is rapidly reshaping how people work in all businesses, regardless of size. In fact, the old stereotype of SMBs as technology laggards no longer fits: SMB Group’s 2016 Top 10 SMB Technology Trends reveal that today, the vast majority of SMBs have more favorable views about technology’s role in their business (Figure 1). Furthermore, Dell’s Global Technology Adoption Index (GTAI 2015) finds that enterprises using new technologies including big data, cloud computing and mobile solutions have up to 53% higher revenue growth rates than enterprises that don’t.
Figure 1: SMBs View Technology as Key to Success
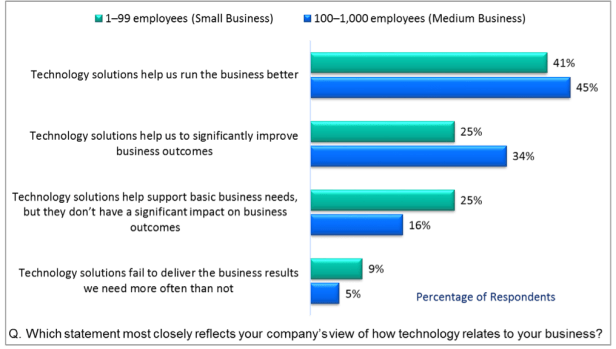
Source: SMB Group 2015 SMB Routes to Market Study
As Reliance on Technology Grows, Security Requirements Become More Complex
Most SMBs understand that data security and management challenges grow as technology becomes a bigger part of the business fabric. Our study shows that both small and medium businesses rank security as their second-most-pressing technology challenge (Figure 2).
Figure 2: Top Technology Challenges for SMBs Source: SMB Group 2015 SMB Routes to Market Study
Source: SMB Group 2015 SMB Routes to Market Study
However, as noted in SMB Group’s 2016 Top 10 SMB Technology Trends, “Security Remains the Elephant in the SMB Room.” SMBs often feel overwhelmed, confused or inadequate to deal with the magnitude of the seemingly endless potential for digital security breaches. The growth of data, mobile solutions, cloud computing and other technologies give users more flexibility and freedom. But with data living in more places, the risk of data loss and leakage rises. Unfortunately, as we put more information into the right hands, we also increase the likelihood of putting it into the wrong ones.
As the sheer magnitude of potential cyber-security risks grows, SMBs that continue to take an outdated, ineffective, 1990s-era “whack-a-mole” approach to security–deploying point solutions to ward off the security threat du jour–are at increasing risk for both accidental and malicious data breaches.
But, SMB Group research indicates that on average, only 22% of businesses with fewer than 100 employees have full-time, dedicated IT staff, and 31% have no IT support at all. Meanwhile, although 85% of medium businesses have dedicated IT staff, these employees are likely to be IT generalists. Given the fact that there are no chief security officers in SMBs, what’s an SMB to do?
Finding Balance: A New Security Approach for SMBs
SMBs need a more comprehensive approach—one that makes security a manageable challenge instead of a bewildering, unsolvable nightmare. They need a solution that enables them to continue taking advantage of the latest mobile, cloud and other technology advancements, and also offers peace of mind that their biggest risks are being managed.
Endpoint security management solutions help close off the biggest vulnerabilities to the most critical corporate data, wherever it resides—whether endpoint devices, mobile apps, on-premises infrastructure and applications or the cloud (Figure 3). Endpoints can include any end-user device, such as smartphones, PCs and tablets, as well as specialized devices such as point-of-sale terminals and bar code readers.
Figure 3: Endpoint Security Management Source: SMB Group 2015 SMB Routes to Market Study
Source: SMB Group 2015 SMB Routes to Market Study
These solutions provide policy-based approach that requires endpoint devices to comply with specific criteria before they are granted access to network resources. For instance endpoint security management solutions:
- Check the status of a user’s device when it connects to the network to ensure that the operating system, browser and other applications are in compliance
- Determine whether security components are up to date.
- Enable policies to be created to set up individual rules for different levels of access to files or applications.
- Are deployed on both the client and server-side, enabling centralized monitoring and management on the server.
- Are often data-centric, meaning that they encrypt and protect the data itself so that it remains protected as it travels across different devices or cloud platforms.
Sponsored by Dell, SMB Group’s free research brief, Finding Balance: A New Security Approach for SMBs, is designed to improve SMB understanding in this area. The brief discusses how endpoint security solutions work; internal considerations to keep in mind when developing an endpoint security strategy; and key capabilities to look for in an endpoint security solution.
Although you can’t eliminate every risk, endpoint security management can offer a more holistic, rules-based approach to face and address the security elephant in your business a more effective way.
This post is sponsored by Dell.


Hi Laurie, Our company, VersAccounts, is interested in talking to you about writing a white paper for us about ERP and small business. Let me know if this is something you would be interested in doing. Thanks,
Traci
On Wed, May 11, 2016 at 12:43 PM, Laurie McCabes Blog wrote:
> lauriemccabe posted: “The Internet, cloud computing and mobile solutions > have empowered people with the freedom and flexibility to do their jobs > more easily and quickly than ever before. At the same time, new > technologies continue to expand the volume and variety of data at ou” >
Hi Traci, i’d be happy to talk to you and see what you have in mind. Can you please email me at laurie.mccabe@smb-gr.com and we can schedule a call. Thanks!